Department of Clinical Neurophysiology (EMG & EP)

| Location | 2ND Floor, MRC |
| For Appointment | 022-22067676 Extn. 374 |
| Dept. Timings | Mon to Sat. 9:00 am to 5:00 pm |
| List of Consultants | Dr. K.A. Mansukhani Dr. Alika Sharma |
This department was established in 1975 by Dr. S.S.Pandya who was trained in U.K. by Prof Buchthal,a pioneer in this field. Dr. Shubha Pandya was the first one to introduce this branch of diagnostic medicine in Mumbai and possibly in the country.
The Electrodiagnostic department at Bombay Hospital is equipped with top of the line equipment. The entire study is performed by doctors trained specially in this branch of medicine.
Electromyograph: The Machine
Electroneuromyography & Nerve Conduction Study (EMG & NCS) also known as Electrodiagnosis, is an assessment of a patient by a physician using a series of tests to establish an accurate diagnosis of a presenting clinical problem that suggests a neuromuscular disorder.
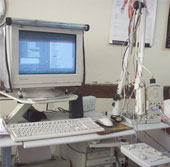
It is an extension of the clinical examination to assess the functional status of the peripheral neuromuscular system and is useful in the diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathies, Cranial neuropathies, Radiculopathies, Neuromuscular junction effects, Myopathies, Nerve Injuries, Plexopathies and Anterior Horn cell diseases.
It is the only test that examines the function of the nervous tissue being examined and is directed by the clinical impression and the working diagnosis (customized for every patient.
- Accurate localization of the site (Nerve, Plexus, Root, muscle, AHC)
- Determining the extent( localised, widespread, Multifocal)
- Identifying the predominant Pathophysiology( Demyelinating, axonal or both)
- Objective quantification of the severity (Mild, Moderate, severe)
- Documents progress of lesion
- Intra operative assessment( for trauma)
Nerve conduction studies- A method of measuring changes in a peripheral nerve by stimulating it electrically and recording the action potential generated.
- Sensory nerve conduction studies
- Motor nerve conduction studies
Electroneuromyography-
A method of studying the electrical activity of a muscle, by placing a needle electrode within it and observing:
- The spontaneous activity in the muscle at rest.
- The action potentials (Motor Unit Action Potentials) generated by voluntary contraction of the muscle. This is an audio visual diagnosis and is done online.
What should your patient expect?
NCS FAQs answered
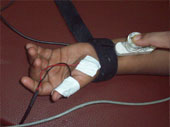
- Nerve Conduction Studies are performed using surface electrodes
- The ‘shocks’ given are in Milli amperes and are quite bearable.
- The stimulus is local and does not travel all over the body
- Nerve Conduction Studies are always required with a Needle Electrode Examinations.
- Can be done very safely even in the new –born & pregnant women.
- The Motor conduction stimulus feels like a tap and causes movement of the area being stimulated
- The Nerve Conduction Studies may be contraindicated in patients with Pacemakers.?
What should your patient expect?
EMG FAQs answered
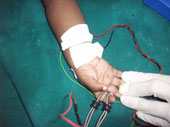
- The Needle EMG examination is done using fine Disposable Electrodes, which are solid pins but thin and very sharp
- No shocks are givenThe Needle is inserted just into the muscle for few seconds
- The Needle is inserted just into the muscle for few seconds
- The patient is asked to contract the muscle and the activity is picked up by the electrode and displayed on the monitor and over a loud speaker –diagnosis is made on-line
- The number of muscles examined depend upon the working diagnosis
- Needle EMG should be avoided in patients with bleeding disorders, Patients on Anticoagulants and when there is local infection
How can the referring Doctor help?
- The working diagnosis or Differential diagnosis should be stated in the referral note
- It helps to customize the procedure.
- Relevant reports and supportive radiography should be sent with the patient
- If the patient is HbsAg or HIV positive/ has a pacemaker or is on Anticoagulants the Electromyographer must be alerted
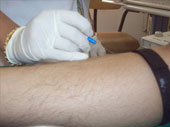
The other tests done in our department are Evoked Potentials which include:
- Visual evoked potentials (VEP)
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEP)
- Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEP)
Visual Evoked Potentials (VEP): Test the optic pathway
- This method currently provides the most sensitive means of detecting subclinical lesions of the optic nerve and may enable a diagnosis of M.S. to be made at an earlier time.
- Abnormality in the Visual Evoked Potentials is also encountered with compressive lesions of the anterior visual pathways.
- In the pediatric age group, the flash VEP may be used as a screening test for the visual pathway.
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials (BAEP): Test the Auditory pathway
- The neurologic applications of Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials have been proven useful in the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis.
- It may be used as a screening test for early detection of acoustic neuromas and in the assessment of comatose patients.
- Like the Visual Evoked Potentials, it may also be a useful screening test for hearing in the pediatric age group such as neonatal screening and those who do not cooperate sufficiently with behavioral testing.
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP): Test spinal cord function
- The Sensory Evoked Potentials findings may help in the detection and localization of lesions of the central somatosensory pathways but are not pathognomonic of specific diseases.
- In Multiple Sclerosis (MS) the presence of Sensory Evoked Potentials abnormalities may reveal subclinical lesions involving the central somatosensory pathways thus aiding in early diagnosis.
- In patients with definite Multiple Sclerosis, the incidence of Sensory Evoked Potentials abnormality is about 80% whereas in the category of possible Multiple Sclerosis, the yield is only about 30%.
- The interpretation of electrophysiological results must therefore always be taken in a clinical context.
AVAILABLE DIAGNOSTIC FACILITIES
- Nerve conduction studies and Electroneuromyography for assessing nerve, muscle, root and plexus disorders in adults
- Neuromuscular diseases in Paediatrics
- Assessment of Birth brachial plexus injuries
- Specialized tests for Neuromuscular Junction Disorders
- Provocative tests for Channelopathies
- Tests for evaluating & prognosticating traumatic nerve / plexus involvement in adults
- Assistance in EMG guided Botulinum toxin injections
- Studies to assess erectile dysfunction & pelvic floor study
- Visual evoked potentials (VEP)
- Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEP)
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials for determining hearing in children (BAEP)
Update: The Maharashtra University of Health Sciences has accredited this department for a fellowship course in the subsection of Electroneuromyography & Evoked Potentials. Interested doctors could look up the details on the MUHS website
Certification Course In Electroneuromyography & Evoked Potential Study
BOMBAY HOSPITAL Department of Clinical Neurophysiology offers a 2-year, certificate course in Electrodiagnostic medicine (Electroneuromyography and Evoked Potential study).
It is a comprehensive 2-year course to train doctors in this field. The program is exhaustive with extensive academic sessions, exams, presentations, and case-based learning.
The course was started in 2008 and till date we have 15 doctors who have completed the course and are practicing in different cities in the country.
Accreditation: Bombay Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Mumbai
Who is eligible: Post-MBBS / MD candidates
How to apply: Download form
Upload completed form: emgdept.bh@gmail.com
About the Program
Aim
To train doctors in the field of Clinical Neurophysiology, to develop expertise in mastering the techniques of the various studies performed integrated with clinical diagnostic skills.
On completion of this training program, the physician would be an independent “clinical neurophysiologist.”
Need for this program
There are only around 2000 neurologists in the country who are busy treating the wide gamete of neurological disorders and serving a population of more than 1.25 crores. Neurophysiology hence takes a back seat and is being relegated to under-trained technologists. We hope to change this trend and train physicians to perform these studies.
Curriculum
The first year of the training begins with orientation in the department. The trainee observes the techniques of NCS, EMG and EPs and maintains a logbook of all the cases observed. Written exams are conducted in the department at the end of each month. Lectures are conducted in the department regularly. Trainee has to participate in monthly departmental presentations and Journal club sessions. Trainee also attends weekly Neurology clinics. After 6 months, the trainee performs NCS and EPs on patients under supervision.
Training is done for expertise in performing and analyzing the following studies:
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS)
- Somatosensory evoked potential studies (SSEP)
- Visual evoked potential studies (VEP)
- Brainstem Auditory evoked potential studies (BAEP)
- Repetitive nerve stimulation test
- Blink reflex
- Needle electromyography (NEE / EMG)
- Single fibre EMG test
- EMG guided botulinum injection therapy (NB: injections given by neurologists)
- Pediatric EDx studies
At the end of 1 year, a written and viva-voce examination is conducted by senior neurologists and Department head.
After the final exam, the doctor is appointed as Medical Officer for 1 year and works in the department.
Faculty:
Dr K A Mansukhani – Department head & Program Director
Dr Alika Sharma – Associate Consultant & Program coordinator
Dr Priyanka Chavan – Junior Consultant & Program coordinator
Teaching and conferences for the Fellows
- Lectures by faculty of the department
- Presentations by the fellow
- Participation in weekly Neurology teaching sessions
- Attending relevant medical conferences & paper/ poster presentations
Research experience
The fellow is required to plan & complete a research project in EDx medicine with the results submitted either as a paper / poster presentation and/ or for publication in a medical journal.
Contact us:
Email: emgdept.bh@gmail.com
Tel: 022 - 40511374
Our Previous Fellows -
- Dr Bhavna Doshi (2000) Mumbai Nanavati Max bhavnadoshi1@gmail.com
- Dr Sangeeta Dhoot (2008) Ahmednagar sangeetadhoot108@gmail.com
- Dr Nishu Ojha (2008) Mumbai
- Dr Mayura Dhonde (2009) Nanded mayuradhonde@gmail.com
- Dr Prajakta Deshmukh (2010) Aurangabad prajaktadeshmukh@yahoo.co.in
- Dr Alika Sharma (2010) Mumbai Bombay Hospital alika.sharma@gmail.com
- Dr Renuka Yadav (2011)Ahmedabad renukarakhil@gmail.com
- Dr Aarthika Sreenivasan (2012) Navi Mumbai draarthika@gmail.com
- Dr Diya Virwani (2012) Akola gbadlani14@gmail.com
- Dr Lajita Balakrishnan (2013) Apollo Vashi lajita.b@gmail.com
- Dr Shweta Chaudhari (2014) Jalgaon achyutshweta@gmail.com
- Dr Priyanka Chavan (2016) Mumbai Bombay Hospital drpriyankachavan29@gmail.com
- Dr Payal Agrawal (2018) Gondhia dr.payalagrawal26@gmail.com
- Dr Kirti Jalela (2019) Rajkot kirti.j2012@gmail.com
- Dr Amretha Nambiar (2022) Mumbai, Bombay Hospital amruth582.aa@gmail.com
Application Form - Download Form
LAB TESTS AT YOUR DOORSTEP

- Say goodbye to the hassle of visiting labs with Bombay Hospital’s reliable home collection service.
- Our skilled technicians ensure a smooth and efficient process, while keeping your health information safe and private.
- With accurate results delivered directly to you, experience the convenience and quality healthcare that comes to you.
For Appointments
📞 +91-8585067676Working Hours
⏰ Available daily from 8 AM to 6 PM
Get the care you deserve, in the comfort of your home.




