Neurological disorders in children can affect their development, learning, and overall quality of life.
Early detection plays a critical role in managing these conditions effectively. Many parents may not
realize
the signs until they become more pronounced.
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better outcomes.
If you notice anything unusual in your child's behavior or development, don't hesitate to consult the
best
neurologist for guidance and support.
In this blog, we will explore the most common neurological disorders in children, how to identify them,
and what steps you can take if you suspect your child needs help.
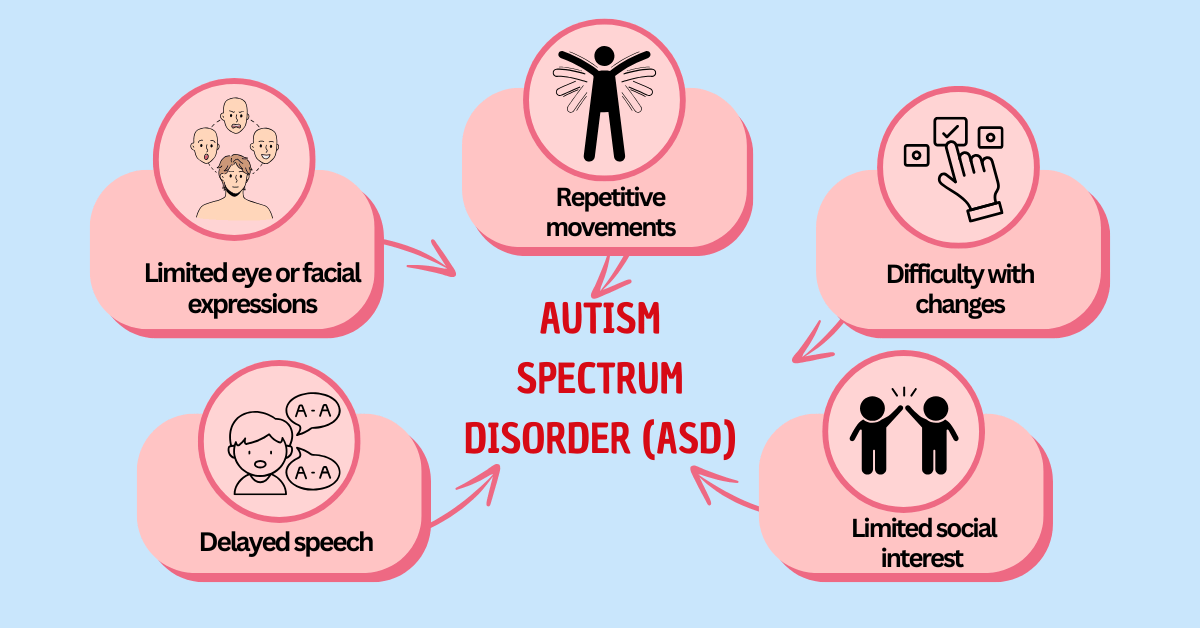
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
What It Is:
ASD is a developmental condition that affects how children interact, communicate, and behave. It
includes a range of symptoms and severity levels.
How to Identify It:
- Delayed speech or language skills
- Limited eye contact or facial expressions
- Repetitive movements like hand flapping or rocking
- Preference for routines and difficulty with changes
- Limited interest in social interactions or play
When to Act:
If your child avoids eye contact, doesn't respond to their name, or shows unusual sensitivity to
sound
or light,
it's time to speak to a pediatric neurologist.
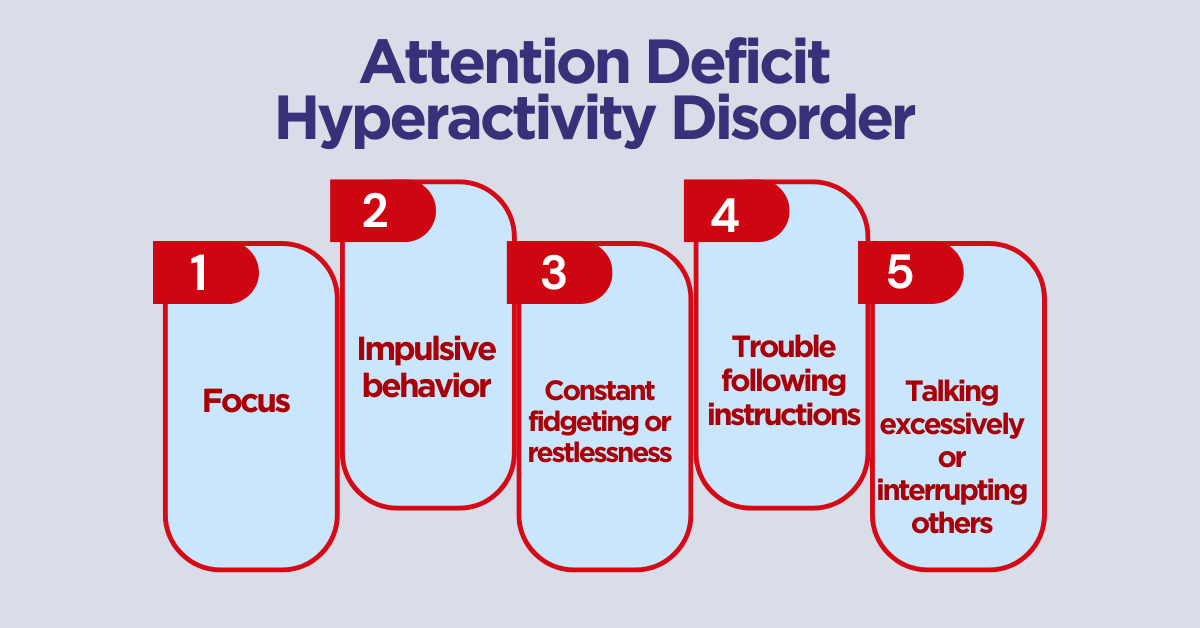
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
What It Is:
ADHD is a disorder that affects attention, self-control, and the ability to sit still or focus.
It can interfere with school performance and daily activities.
How to Identify It:
- Difficulty staying focused
- Impulsive behavior
- Constant fidgeting or restlessness
- Trouble following instructions
- Talking excessively or interrupting others
When to Act:
If teachers mention problems with focus, behavior, or distractibility,
or if your child’s energy levels seem extreme compared to others,
consult a specialist.
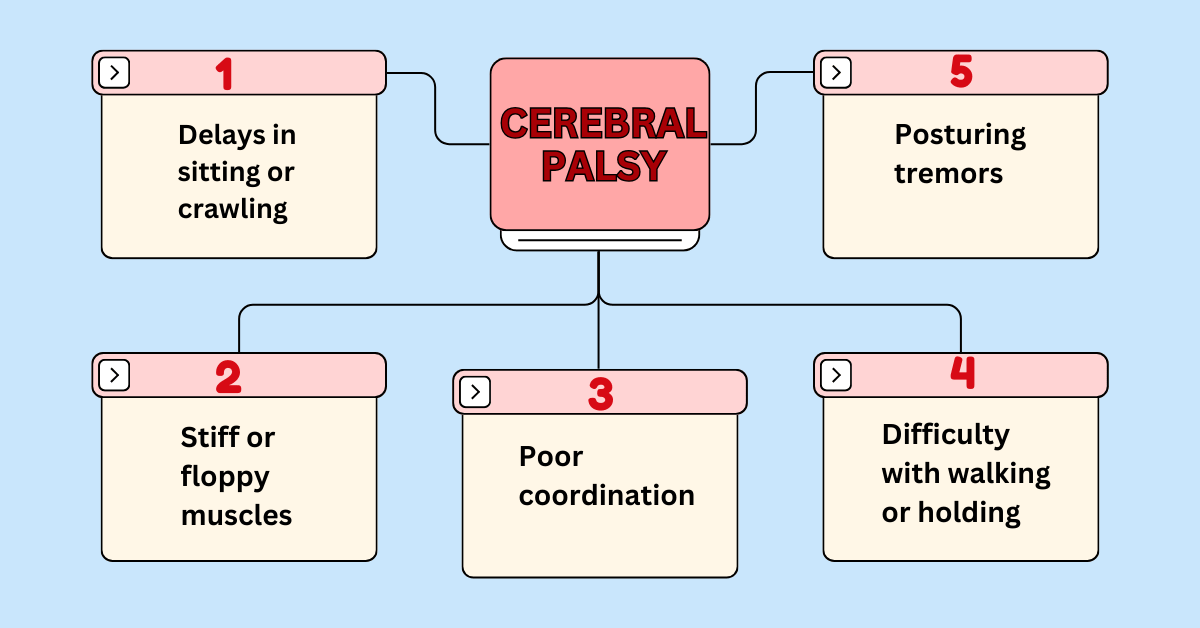
Cerebral Palsy (CP)
What It Is:
Cerebral Palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement, balance, and posture.
It is caused by abnormal brain development or brain damage before, during, or shortly
after birth, including cases where the child did not cry immediately after birth or
there was no history of fever.
How to Identify It:
- Delays in reaching movement milestones like sitting or crawling
- Stiff or floppy muscles
- Poor coordination
- Difficulty with walking or holding objects
- Muscle spasms or tremors
When to Act:
If your child misses important motor milestones, or if their movements appear
rigid or shaky, seek a medical evaluation.
Migraine and Pediatric Headaches
What It Is:
Some children experience frequent headaches or migraines that can
interfere with school performance and daily activities.
How to Identify It:
- Complaints of head pain, usually unilateral
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Dizziness
- Aura symptoms such as seeing flashing lights or blind spots
When to Act:
If headaches affect school, sleep, or play, or if symptoms worsen
rapidly, a neurological evaluation is recommended.
Bombay Hospital and Medical Research Centre, established in 1952 by Shri Rameshwardas Birla,
stands at the heart of Mumbai, India's medical capital. Specializing in areas like Cardiology,
Gastroenterology, Neurology, Urology, Oncology, and more, Bombay Hospital offers expert
consultation and advanced care, including routine liver testing and specialized treatment for
conditions like cirrhosis and cancer.
FAQ
Not all are curable, but many can be managed effectively with early intervention,
medication,
therapy, and support.
Some can be noticed as early as infancy. Regular pediatric check-ups help track
development and
identify any red flags.
A single seizure may be due to fever or other triggers. Recurrent seizures should be
evaluated
for epilepsy.
Stay calm, seek a specialist, follow the treatment plan, and consider therapy or support
groups
if needed.
Some children improve significantly over time with intervention. Others may continue to
need
support into adulthood.
Final Thoughts
Children's neurological health is closely linked to their future growth and quality of life. The
earlier you spot signs and take action, the better the outcome. Knowing what to look for helps you
make informed decisions. If something seems off, don't wait. Trust your instincts and reach out to
experts. Support, care, and early treatment can make all the difference in your child's journey.